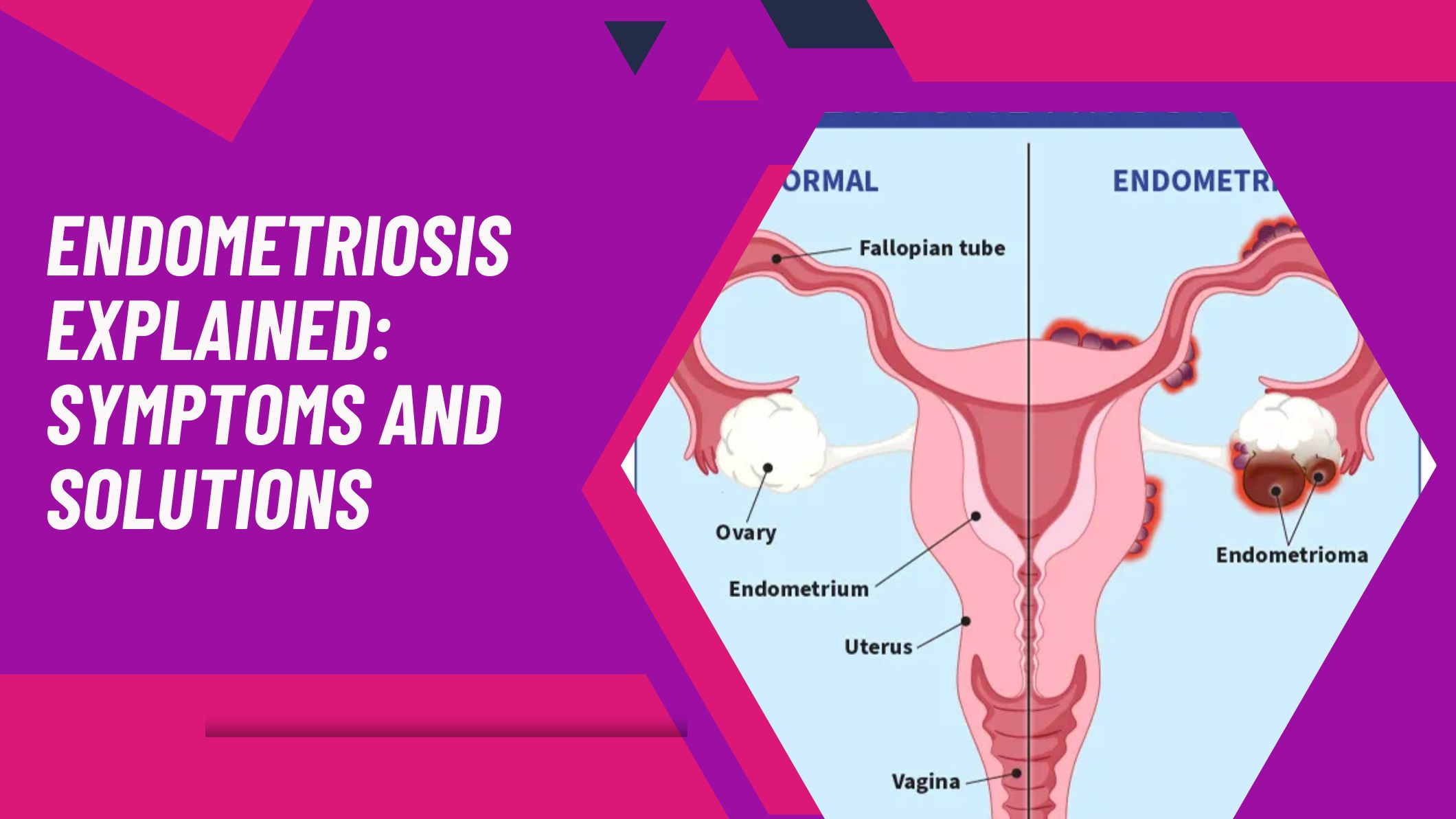
Endometriosis is a chronic condition that affects millions of women worldwide. It occurs when the tissue similar to the lining of the uterus (called the endometrium) starts to grow outside the uterus. These misplaced tissues can be found on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and even other organs in the pelvic region, leading to inflammation, pain, and sometimes fertility challenges. Understanding the symptoms and exploring effective treatment options can help women manage this condition and improve their quality of life.
Understanding the Symptoms of Endometriosis
The symptoms of endometriosis can vary from mild to severe and often depend on the extent of tissue growth. One of the most common signs is pelvic pain, particularly during menstruation. Unlike regular menstrual cramps, this pain tends to be more intense and persistent. Other symptoms include:
- Pain during or after sexual intercourse
- Excessive bleeding during or between menstrual periods
- Lower back or abdominal pain
- Digestive issues such as bloating, constipation, or nausea
- Fatigue and general weakness
- Infertility or difficulty conceiving
It’s important to note that the severity of symptoms doesn’t always correlate with the extent of the disease. Some women with advanced endometriosis may experience mild discomfort, while others with early stages can have severe pain. Because symptoms can mimic other conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), many women go undiagnosed for years.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosis of endometriosis begins with a detailed medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI. However, the most definitive way to diagnose endometriosis is through a laparoscopy—a minimally invasive surgical procedure where a small camera is inserted into the pelvic area to detect and possibly remove endometrial tissue.
Treatment depends on the severity of symptoms, the patient’s age, and whether she plans to have children. Common treatment options include:
1. Medication Management
Pain relievers like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often the first line of defense to manage discomfort. Hormonal therapy—such as birth control pills, progesterone therapy, or gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists—can help regulate or stop menstruation, reducing the growth of endometrial tissue and relieving pain.
2. Surgical Treatments
For severe cases, surgical removal of endometrial implants can provide long-term relief. Laparoscopic excision surgery is considered the gold standard for endometriosis treatment as it allows precise removal of the lesions while preserving fertility whenever possible. In extreme cases, hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) may be recommended if other treatments fail and symptoms persist.
3. Lifestyle and Supportive Therapies
Lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in managing endometriosis. Regular exercise, stress management, and a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help reduce flare-ups. Alternative therapies such as acupuncture, yoga, and physiotherapy may also provide relief from chronic pain. Counseling or joining support groups can further help patients cope with the emotional and psychological challenges associated with the condition.
Living Well with Endometriosis
While endometriosis can be a lifelong condition, early diagnosis and personalized endometriosis treatment can help women lead fulfilling lives. Continuous medical supervision and a supportive healthcare team are essential for effective symptom management. Women are encouraged to track their symptoms, seek timely medical advice, and stay proactive in their treatment journey.
If you are experiencing symptoms of endometriosis or need expert consultation, Dr. Preeti Tandon provides the best services and personalized treatment plans to help you regain comfort, balance, and reproductive health. With compassionate care and advanced medical expertise, she ensures every patient receives the attention and treatment they truly deserve.



